
Hand and wrist > Training resources
Occupational hazard for respiratory therapists and house staff who work around oral secretions. (Image Credit)



Ehlers Danlos, many types. Syndrome may include skin hyperextensible, fragile, "cigarette paper burn" scars, spontaneous rupture of eye, arteries, intestine, hip dislocations, Marfanoid habitus, kyphoscoliosis, prominent hernia, mitral valve prolapse, coronary dissection.
Ellis Van Creveld Syndrom - dwarfism, short extremities and polydactyly, dysplastic teeth and nails, multiple frenula binding the upper lip to the alveolar ridge, ASD or a single atrium.
Long "spider-like" digits, thumb can often extend beyond palm. Characteristic of Marfan's Syndrome - tall stature, thoracic deformity, joint laxity, ectopia lentis and myopia, aortic dilation and dissection, mitral valve prolapse, autosomal dominant, spontaneous pneumothorax, chordae tendineae rupture.
Thickened, velvety texture of hand. Often sign of visceral malignancy. See also NEMJ "Velvet Palms" in Images in Clinical Medicine. (Image Credit)


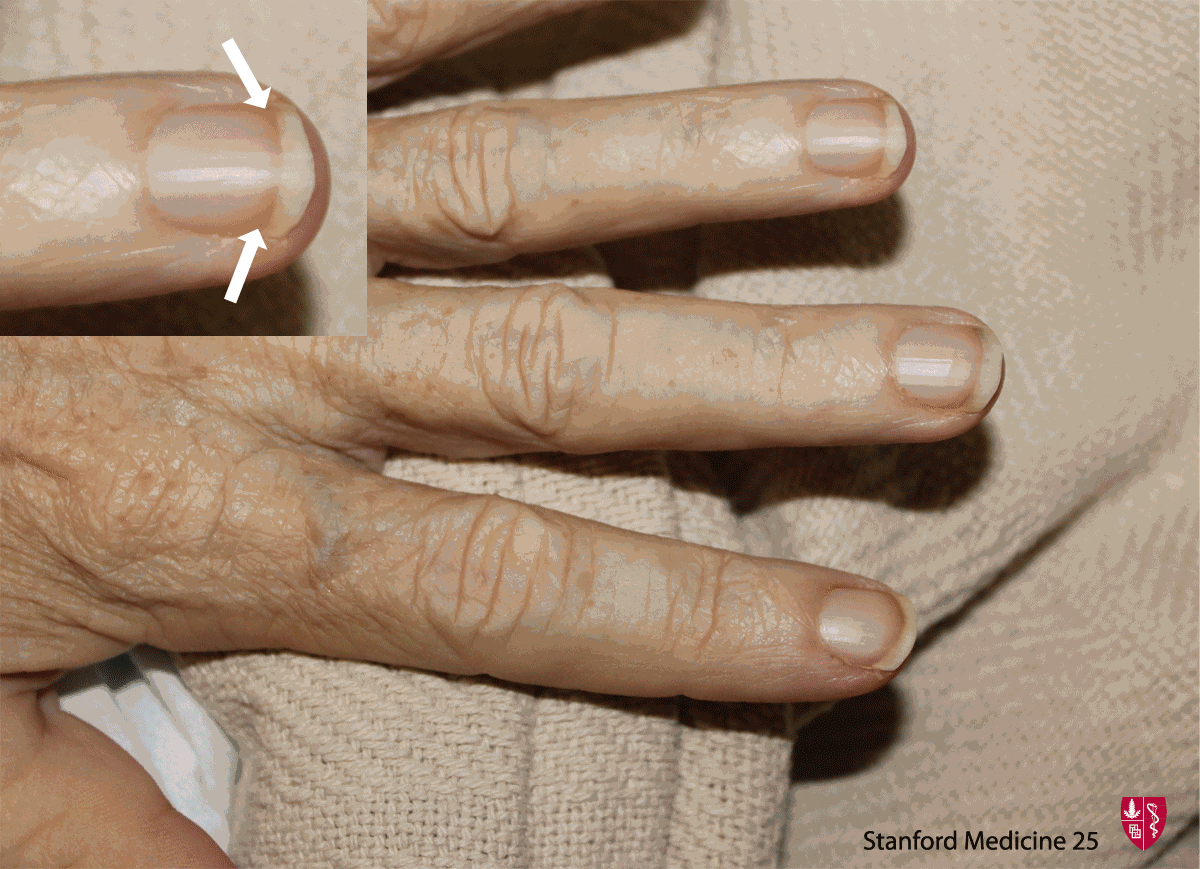
Proximal paleness extending halfway up the nail, often eliminating the lunula. Darker distal band. Seen in states of stress (e.g. advanced age, liver disease/cirrhosis, CHF, DM2). (Image Credit)
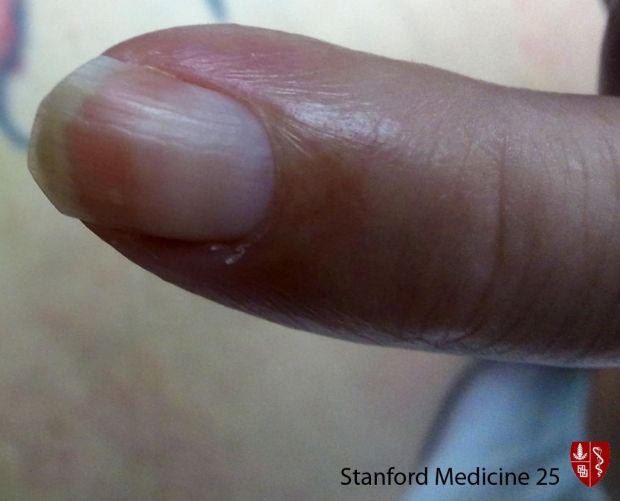

Narrow while transverse lines (Not depressed, compared to Beau's lines). Usually 2 or more lines on one nail. Seen in states of decreased protein synthesis or increase protein loss such as with hypoalbunemia (usually less than < 2.2 g/dL), certain chemotherapy and nephrotic syndrome. (Image Credit)

Transverse while lines (usually one per nail, no depressions) that often can will disappear if pressure is placed over the line. It is strongly associated with arsenic poisoning, thallium poisoning and to a lesser extent other heavy metal poisoning. (Image Credit)


Nonspecific finding associated with trauma most commonly but also seen in subacute bacterial endocarditis and scleroderma. (Image Credit)

Non-specific sign for psoriasis (additional signs include onycholysis, thickening, and 'oilspot' lesions which are yellow patches on the nail). (Image Credit)

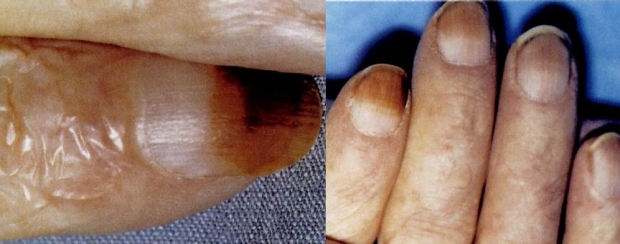
Nicotine stained distally, but not proximally with clear line of demarcation. See also our article in Chest and NEJM clinical image. May also appear when pt switches to "lower tar" tobacco.


Inflammation of the nail folds - red, swollen, often tender. Frequent immersion in water a risk factor for chronic paronychia. (Image Credit)


Important causes of clubbing in the adult:
Pseudoclubbing: distinguished from clubbing by the preservation of the nail-fold angle and bony erosion of the terminal phalanges on radiography. Pseudoclubbing is also more likely to be asymmetric.
The pope's hand is seen with median nerve dysfunction when asking the patient to make a fist due to inability to flex 1st & 2nd fingers at PIP. The median nerve controls the 1st & 2nd lumbricals, three thenar muscles (abductor pollicis brevis, flexor pollicis brevis, and via a distal branch the opponens pollicis).Additionally theremay be thenar atrophy. (Image Credit)
Ask patient to use both hands to make and "Okay" sign by forming a circle with thumb and index finger. Median nerve palsy may make one hand produce a pinched circle (right hand in image). (Image Credit)

Ape Hand
Distal median nerve dysfunction: Inability to oppose thumb from distal median nerve dysfunction.
The image below is a simulated claw hand. Note that due to ulnar damage, the 3rd & 4th lumbricals are unable to extend the PIP & DIP joints at the 4th & 5th digits.
The ulnar nerve controls the 3rd & 4th lumbricals, the three hypothenar muscles, the dorsal & palmar interossei, the palmaris brevis and the adductor pollicis. Ulnar nerve damage may also cause hypothenar atrophy.

Ask patient to hold a piece of paper between thumb and index finger. If the examiner can pull paper away (a positive Froment's sign), it suggests that an ulnar palsy has weakened the thumbs strength of opposition.
No intrinsic muscles but important wrist extensors. Radial nerve damage commonly causes wrist drop.
